Radiation Transport Setup
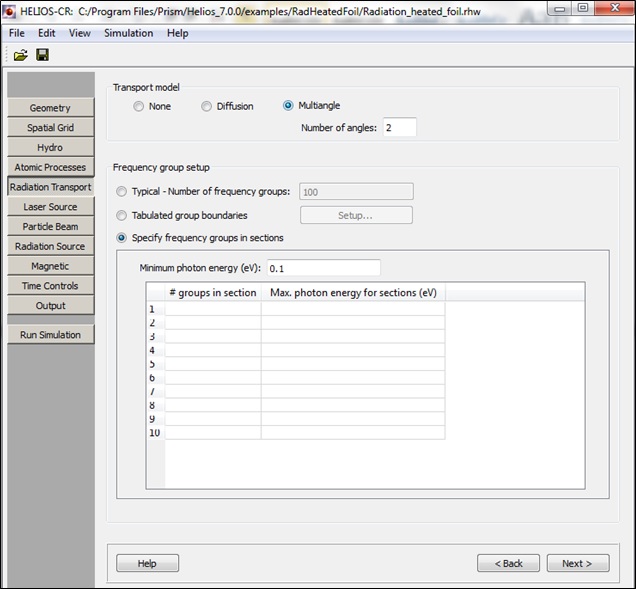
Radiation transport is performed using one of the following:
- A multi-group, flux-limited diffusion model
- A multi-group, multi-angle long characteristics model.
At present, the multi-angle model can be utilized only
in planar or spherical geometry. When selecting the multi-angle model, the number of angles
must be specified. For planar geometry, the number of angles is limited to a discrete set of options. For spherical geometry, the number is not restricted. In this case, accuracy will improve with a larger number of angles, at the cost of longer computation time. Increasing the number of angles beyond the number of zones will likely not improve the accuracy.
The binning, or distribution, of frequency (i.e., photon energy) groups
is set up using one of the following approaches:
- Typical: Using the specified number of frequency groups, a grid is
set up with approximately 85% of the groups having photon energies between
0.1 eV and 3 KeV, while the remaining 15% lie between 3 KeV and 1 MeV.
- Tabulated Group Boundaries: The boundaries of the frequency groups
are entered into a table or the table values can be imported from a file.
The table is accessed by clicking the Setup button. See Entering Table
Data for information about entering or importing data.
- Specify Frequency Groups in Sections: The spectrum is divided into "sections" (or spectral ranges), the number of which is given by the number of filled table rows. For each section, the number of groups and the upper bound of each section of groups is specified. This allows the user to specify high frequency resolution in one spectral range, and a coarser frequency resolution in another range.
Next
| Copyright
© 2002-2025 Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. |
HELIOS 11.0.0 |