| CONTENTS | GLOSSARY | SUBJECT INDEX | SEARCH DOCUMENTATION |
In this calculation, an external radiation source drives a strong shock through an Al plate.
Setup:
Choose geometry: select Planar and click Next.
Setup Spatial Grid. The steps for this relatively complex dialog are:
Click New region.
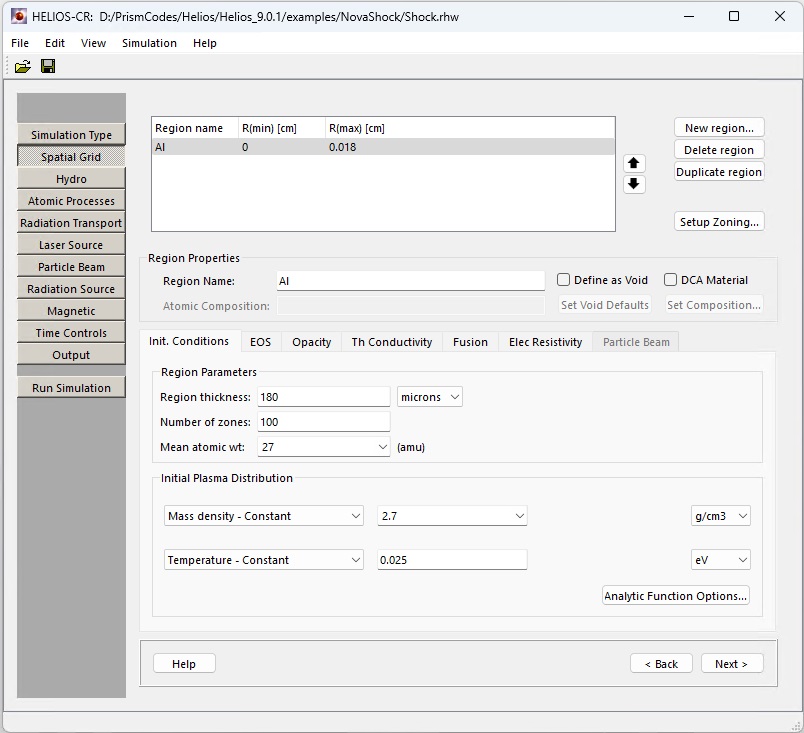
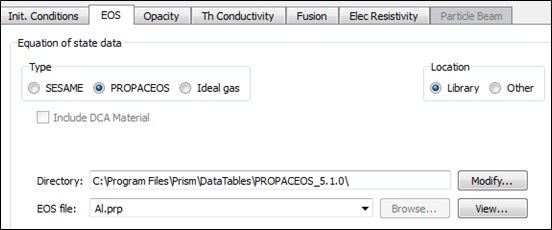
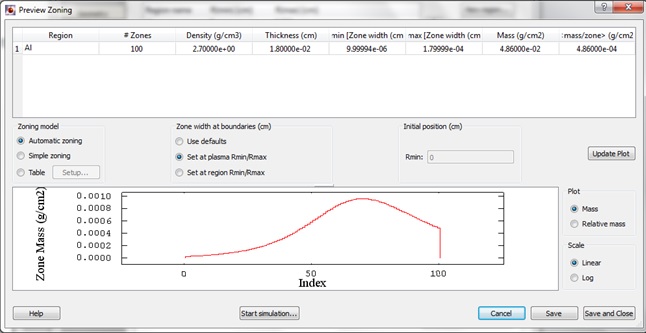
Select tab Init. Conditions and click setup zoning.
The radiation transport is performed using one of the following: a multi-group, flux-limited Diffusion model (most commonly used in rad-hydro codes), or a multi-group, Multiangle long characteristics model (more accurate, but potentially slower), or None – radiation transport is ignored. The radiation heating and cooling will still be computed. At present, the multi-angle model can be utilized only in planar geometry.
The binning, or distribution, of frequency (i.e., photon energy) groups is set up using one of the following approaches. Typical: using the specified number of frequency groups, a grid is set up with approximately 85% of the groups having photon energies between 0.1 eV and 3 KeV, while the remaining 15% lie between 3 KeV and 1 MeV. Tabulated Group Boundaries: the boundaries of the frequency groups are entered into a table or the table values can be imported from a file. Specify Frequency Groups in Sections: the spectrum is divided into "sections" (or spectral ranges), the number of which is given by the number of filled table rows. For each section, the number of groups and the upper bound of each section of groups is specified. This allows the user to specify high frequency resolution in one spectral range, and a coarser frequency resolution in another range.
Leave Laser Source parameters unchanged and click Next.
An external radiation source can be applied to the hydro grid boundaries during simulation. For planar geometries an external source can be applied at the inner boundary (R(min)) and/or the outer boundary (R(max)). For cylindrical and spherical geometries, an external source can only be applied at the outer boundary. The time-dependence of the flux is based on interpolated radiation temperatures from the 1 - T table. The photon energy-dependence is determined assuming a Planckian source with a temperature given by the radiation temperature.
If the Magnetic parameters are available, leave them unchanged and click Next.
Setup Time Controls: enter 2.5e-9 in Max. simulation time field and click Next.
Setup Output: enter 2e-11 in the table (column Output every), save the file, and then press Run Simulation.
In Preview zoning dialog make sure that the zoning is good, and press Start simulation.
In the confirmation dialog select Run Directory, Run Name, and click OK.
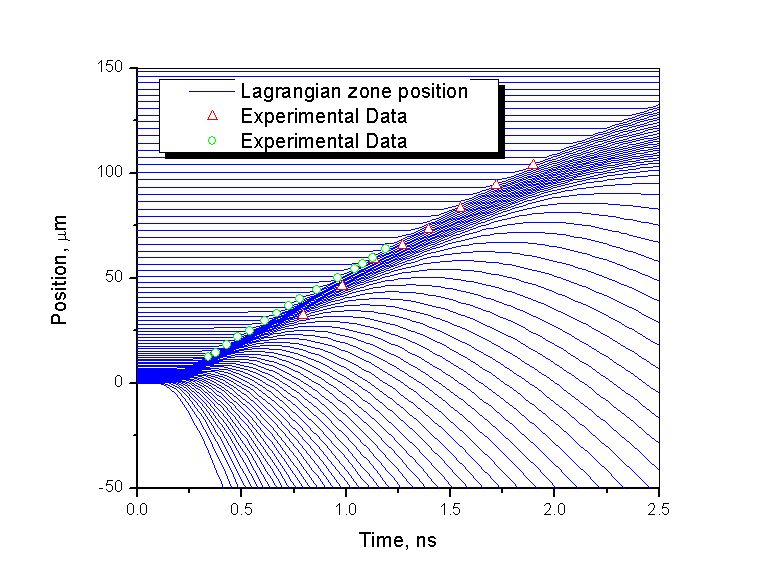
Example Simulation Results: Lagrangian zone position diagram (RT-diagram), showing shock propagation in Al plate, along with the experimental data*.
____________________________________
* Experimental data from NOVA experiments, courtesy of R. E. Olson (Sandia National Laboratories).
| Copyright © 2002-2025 Prism Computational Sciences, Inc. | HELIOS 11.0.0 |